1. What They Are
- RGB
- Stands for Red–Green–Blue
- An additive color model: combining red, green, and blue light produces white, absence of light is black
- Used on digital screens—monitors, phones, tablets
- CMYK
- Stands for Cyan–Magenta–Yellow–Key (Black)
- A subtractive color model: inks absorb (subtract) light; layering all inks creates black
- Used in printing—flyers, posters, packaging
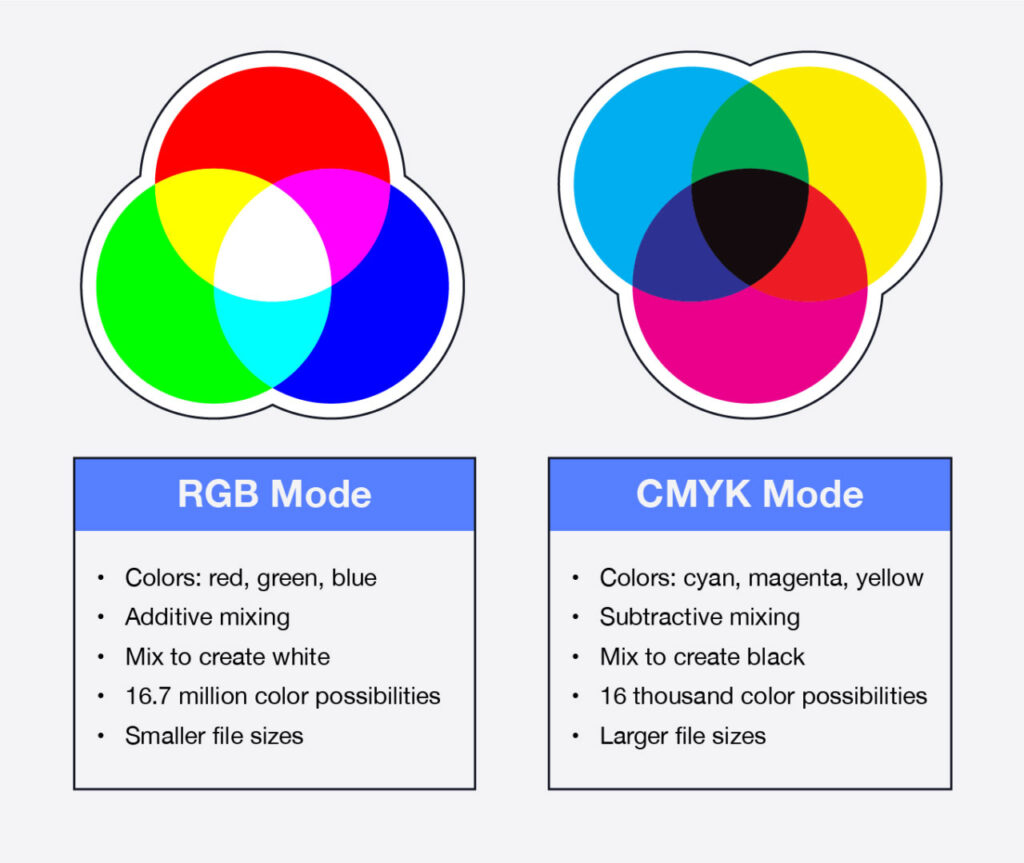
2. How They Work
| Feature | RGB | CMYK |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing process | 🔆 Light-based; add colors to brighten | 🖨 Ink-based; subtract colors from white |
| Primary colors | Red, Green, Blue | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black |
| Color output | Up to 16.7 million vibrant hues | About 16,000 printable shades |
| File size | Generally smaller | Usually larger due to extra ink data |
3. When to Use RGB
- Best for digital projects: web design, apps, social media graphics, GIFs, videos
- Ideal for vivid visuals that “pop” on screens
- Easier to manipulate and upload due to smaller file sizes
4. When to Use CMYK
- Essential for printing: business cards, brochures, posters, packaging, apparel prints
- Ensures accuracy in printed color—printers interpret CMYK directly, avoiding color shifts
5. Common Pitfalls & Tips
Don’t start with RGB if final output is print!
- Converting RGB→CMYK late may mute colors and distort your design
- Always work in the final medium’s color mode: RGB for screens, CMYK for print
Check the mode in your software:
- In Photoshop: Image → Mode
- Illustrator: File → Document Color Mode
- InDesign: Window → Color
Need to convert?
- Use color-managed conversions with appropriate ICC profiles—or better yet, work in CMYK from the start to avoid surprises
Why It Matters
- Brand consistency: Colors must look as intended, whether on-screen or in-print
- Don’t disappoint clients: Online-looking artwork can appear dull when printed
- Save money & time: Avoid reprints due to unexpected color issues
Quick Reference
- 🖥️ RGB = Digital + screen + light + vibrant
- 🖨️ CMYK = Print + physical + ink + realistic
Visual Breakdown
- Venn-style comparison of RGB vs CMYK
- Side-by-side circle mixing diagrams (light vs ink)
- File export workflow each mode
- Real-world applications: web vs print
Suggested Blog Structure
- Intro – Why you must choose the right color model
- Definitions – Clear show, don’t just tell
- Technical walkthrough – How each mixing model works
- Practical advice – When to use which
- Tools check – Where to verify your color mode
- Conversion tips – Handling mode changes gracefully
- Conclusion – Smart color = smarter design
Suggested Visual Assets
- Infographic summarizing key differences (use provided carousel images)
- Color mixing diagrams: light + pigment visuals
- Real design previews: how RGB designs print vs digital
Elevate Your Brand Packaging
Craft packaging that makes your products shine
Get started today!



